Overview
Intent Output allows data acquired and processed by DataWedge to be sent to the associated foreground application as payload within an Android intent object. This allows acquired data to be passed programmatically to an application, where it can be consumed or further processed. The core components of an application (its activities, services and broadcast receivers) also can be activated by intents, as can many DataWedge features through the DataWedge APIs.
The Intent Object
An intent object is a bundle of information that describes a desired action. It includes the data to be acted upon, the category of component that should perform the action and other pertinent data and/or instructions. When an intent is initiated, Android locates an appropriate component to respond to the intent, launches a new instance of the component (if needed), and passes the intent object to it.
Components advertise their capabilities (the kinds of intents they can respond to) through intent filters. Since the system must learn which intents a component can handle before it launches the component, intent filters are specified in the app's AndroidManifest.xml file as <intent-filter> elements. A component can have any number of intent filters, each describing a different capability.
For example, if the manifest contains...
<intent-filter>
...
<action android:name="android.intent.action.DEFAULT" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.MAIN" />
</intent-filter>
...the intent action in the Intent Output configuration would be:
android.intent.action.DEFAULT
and the Intent category would be:
android.intent.category.MAIN
Outputting Raw Data
In addition to its normal plain-text and hexadecimal modes, DataWedge can output acquired data in its raw form, before the application of any encoders. This can be useful if custom encoders are needed for acquiring character sets not supported by Zebra.
Raw data is received as a byte stream using the com.symbol.datawedge.decode_data intent extra. See the Single Decode Mode section below.
Raw data cannot be output as keystrokes.
Intent Output Setup
DataWedge invokes an intent though an Intent action in an Intent category as described in its AndroidManifest.xml file.
When combined, these two values are like a "channel" to which an app can listen for intents that use the same combination, filtering out "noise" from other intents that use different value pairs. Once these values are known, DataWedge Intent Output must be set to match.
Component Information specifies the package names and signatures of the applications that are designated to receive intent data. This adds a level of security to guarantee that data is delivered only to the intended applications.
When the package name is specified, DataWedge sends explicit intents only to the package name. Optionally, enabling the application signature check adds another level of security for intent delivery. DataWedge matches the signature of the application before sending out the intent. If the signature does not match, DataWedge does not send the intent. If the signature check is not enabled, DataWedge sends the explicit intent based on the package name.
For example, if a package name is specified as 'com.zebra.app1' without the signature check, another app can be created with this same package name and disguised as the original - the original app can be uninstalled on the device and the new malicious app can be installed as the replacement. This results to the intent data being delivered to the malicious app. If instead, the signature check was enabled for the original app, even though the new app shares the same package name, the signature is different and therefore the intent data cannnot be delivered to the malicious app.
Use content providers option allows applications to leverage DataWedge's content provider to retrieve scanned data from files larger than 500 KB, such as images, primarily with Signature Capture and NextGen SimulScan. A content provider is an Android app component that encapsulates data to share between apps.
The parameters of these features can be configured through the UI or by using the Set Config API.
See Use Content Provider Programmer's Guide for more information.
Important: For scanning applications that output directly to an activity, the activity must be designated as "singleTop" in the app's
AndroidManifest.xmlfile. Failure to designate an activity in this way will cause an instance of the activity to be launched with every decode, and the acquired data sent to each newly spawned instance.
To configure DataWedge with Intent Output options:
1. Locate the Intent Output section of the Profile being configured.
2. Check "Enabled" box to activate Intent Output:
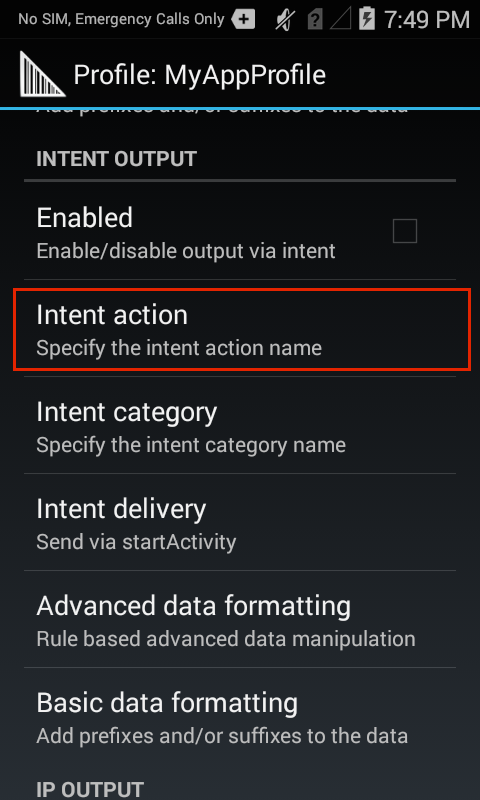 Intent Output options for the "Launcher" Profile
Intent Output options for the "Launcher" Profile
3. Specify action, category and delivery as described below:
Intent action - specifies the action to handle the intent
Intent category - specifies the category of intent to be handled
Intent delivery - used to select one of four delivery methods for intent-based data:
- Send via startActivity - startActivity() Android API is called to deliver data.
- Send via startService - delivers data using Android's startService() API. This method is recommended only if your application/service is compiled for Android SDK version 25 or below. If your application/service is compiled for SDK version 26 or above, startService() option does not work. Refer to startService Android developer article.
- Send via startForegroundService - startForegroundService() Android API is called to deliver data. This option applies to Android Oreo (v8.0) and above. This method is recommended only if your application/service is compiled for Android SDK version 30 or below. If your application/service is compiled for SDK version 31 or above, startForegroundService() option does not work. Refer to startService Android developer article.
- Broadcast Intent - Receiver foreground flag
Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_FOREGROUNDcan be set giving the broadcast recipient permission to run at foreground priority with a shorter timeout interval. Zebra recommends using this flag only if delays are seen in delivery of intents immediately following device boot-up.
4. Specify component information for secure intent delivery. Tap on Component Information.
 Component Information under Intent Output
Component Information under Intent Output
Tap the top right menu and select New Component.
 Add New Component
Add New Component
Select the package name to receive intent data from the installed app list.
 Select New Component
Select New Component
When prompted, tap OK to enable the application signature check, allowing DataWedge to retrieve the app signature via the .APK and use it for comparison. Otherwise, tap Cancel. If multiple signatures are available for an app, a list is be displayed for the user to select one signature.
 Application signature
Application signature
The selected package name is listed with an indication whether the signature check is enabled/disabled.
 Component Information list
Component Information list
5. Enable Use Content Providers from the Intent Output screen when scanning large data such as images (for example with Signature Capture and NextGen SimulScan).
 Use Content Providers
Use Content Providers
Single Decode Mode
Single mode reads and decodes a single barcode at a time, and is the most common decoding mode. For decoding multiple barcodes simultaneously, such as with UDI-compliant objects, see UDI/Multiple Decode Mode.
Parameters
Name: "com.symbol.datawedge.source"
Type: [String]
Contents: Source of incoming data
Possible values:
- "msr"
- "scanner"
- "simulscan"
- "serial"
- "voice"
- "rfid"
NOTE: Source of incoming data is "scanner" for camera, imager or scanner.
Name: "com.symbol.datawedge.label_type"
Type: [String]
Contents: Barcode label type (i.e. "EAN128")
Possible values:
- "LABEL-TYPE-CODE39"
- "LABEL-TYPE-CODABAR"
- "LABEL-TYPE-CODE128"
- "LABEL-TYPE-D2OF5"
- "LABEL-TYPE-IATA2OF5"
- "LABEL-TYPE-I2OF5"
- "LABEL-TYPE-CODE93"
- "LABEL-TYPE-UPCA"
- "LABEL-TYPE-UPCE0"
- "LABEL-TYPE-UPCE1"
- "LABEL-TYPE-EAN8"
- "LABEL-TYPE-EAN13"
- "LABEL-TYPE-MSI"
- "LABEL-TYPE-EAN128"
- "LABEL-TYPE-TRIOPTIC39"
- "LABEL-TYPE-BOOKLAND"
- "LABEL-TYPE-COUPON"
- "LABEL-TYPE-DATABAR-COUPON"
- "LABEL-TYPE-ISBT128"
- "LABEL-TYPE-CODE32"
- "LABEL-TYPE-PDF417"
- "LABEL-TYPE-MICROPDF"
- "LABEL-TYPE-TLC39"
- "LABEL-TYPE-CODE11"
- "LABEL-TYPE-MAXICODE"
- "LABEL-TYPE-DATAMATRIX"
- "LABEL-TYPE-QRCODE"
- "LABEL-TYPE-GS1-DATABAR"
- "LABEL-TYPE-GS1-DATABAR-LIM"
- "LABEL-TYPE-GS1-DATABAR-EXP"
- "LABEL-TYPE-USPOSTNET"
- "LABEL-TYPE-USPLANET"
- "LABEL-TYPE-UKPOSTAL"
- "LABEL-TYPE-JAPPOSTAL"
- "LABEL-TYPE-AUSPOSTAL"
- "LABEL-TYPE-DUTCHPOSTAL"
- "LABEL-TYPE-FINNISHPOSTAL-4S"
- "LABEL-TYPE-CANPOSTAL"
- "LABEL-TYPE-CHINESE-2OF5"
- "LABEL-TYPE-AZTEC"
- "LABEL-TYPE-MICROQR"
- "LABEL-TYPE-US4STATE"
- "LABEL-TYPE-US4STATE-FICS"
- "LABEL-TYPE-COMPOSITE-AB"
- "LABEL-TYPE-COMPOSITE-C"
- "LABEL-TYPE-WEBCODE"
- "LABEL-TYPE-SIGNATURE"
- "LABEL-TYPE-KOREAN-3OF5"
- "LABEL-TYPE-MATRIX-2OF5"
- "LABEL-TYPE-OCR"
- "LABEL-TYPE-HANXIN"
- "LABEL-TYPE-MAILMARK"
- "MULTICODE-DATA-FORMAT"
- "LABEL-TYPE-GS1-DATAMATRIX"
- "LABEL-TYPE-GS1-QRCODE"
- "LABEL-TYPE-DOTCODE"
- "LABEL-TYPE-GRIDMATRIX"
- "LABEL-TYPE-UNDEFINED"
Name: "com.symbol.datawedge.data_string"
Type: [String]
Contents: Acquired barcode characters
Example: "abcde12345"
Name: "com.symbol.datawedge.decode_data"
Type: [List <byte [ ]>]
Contents: Acquired raw (unmodified) data as an array list of byte arrays
Example: List_Item_1(array_1(byte11,byte12,byte13)),List_Item_2(array_2(byte21,byte22,byte23)) ...
Sample code:
ArrayList<byte[]> rawData =
(ArrayList <byte[]>) initiatingIntent.getSerializableExtra("com.symbol.datawedge.decode_data");
if (rawData != null)
{
byte[] rawBytes = rawData.get(0);
for (int i = 0; i < rawBytes.length; i++)
Log.d(LOG_TAG, i + ": " + rawBytes[i]);
}
Name: "com.symbol.datawedge.decoded_mode"
Type: [String]
Contents: Mode used to decode the incoming data
Possible values:
- "multiple_decode"
- "single_decode"
UDI/Multiple Decode Mode
When decoding a UDI-compliant object, data is acquired from multiple barcodes simultaneously and output as a multi-decode bundle, which differs from a single-decode bundle. DataWedge also can acquire multiple non-UDI barcodes in a single scan. This section applies to both modes.
Parameters
Name: "com.symbol.datawedge.decode_mode"
Type: [String]
Contents: Mode used to decode incoming data
Possible values:
- "multiple_decode"
- "single_decode"
Name: "com.symbol.datawedge.smart_decode_type"
Type: [String]
Contents: Decode type
Possible values:
- “udi”
- “multibarcode”
Name: "com.symbol.datawedge.data_string"
Type: [String]
Contents: Acquired barcode characters
Example: "abcde12345"
Name: "com.symbol.datawedge.decode_data"
Type: [List <byte [ ]>]
Contents: Acquired raw (unmodified) data as an array list of byte arrays
Example: List_Item_1(array_1(byte11,byte12,byte13)), List_Item_2(array_2(byte21,byte22,byte23)) ...
Name: "com.symbol.datawedge.source"
Type: [String]
Contents: Source of incoming data
Possible values:
- "msr"
- "scanner"
- "simulscan"
Name: "com.symbol.datawedge.label_id"
Type: [String]
Contents: UDI type of incoming data
Possible values:
- “UDI_HIBCC”
- “UDI_GS1”
- “UDI_ICCBBA”
- “UNDEFINED”
Name: "com.symbol.datawedge.barcodes"
Type: [List <Bundle>]
Contents: See Bundle description (below)
Name: "com.symbol.datawedge.tokenized_data"
Type: [List <Bundle>]
Contents: See Bundle description (below)
Note: Source of incoming data is "scanner" for camera, imager or scanner
Barcode Bundle
Bundle name: "com.symbol.datawedge.barcodes"
Parameters
Name: "com.symbol.datawedge.label_type"
Type: [String]
Contents: Barcode label type, original symbology (i.e. "EAN128")
Name: "com.symbol.datawedge.decode_data"
Type: [byte [ ] ]
Contents: Acquired raw (unmodified) data as a byte array
Name: "com.symbol.datawedge.data_string"
Type: [String]
Contents: Acquired barcode characters
Example: "abcde12345"
Tokenized Data Bundle
Bundle name: "com.symbol.datawedge.tokenized_data"
Parameters
Name: "token_id"
Type: [String]
Contents: Data in a UDI-defined tag
Possible values: (see token IDs, below)
Name: "token_data_type"
Type: [String]
Contents: Incoming data type
Example: date, long, string
Name: "token_format"
Type: [String]
Contents: Format of incoming string
Example: YYYYMMDD
Name: "token_string_data"
Type: [String]
Contents: Acquired barcode characters
Example: "abcde12345"
Name: "token_binary_data"
Type: [byte [ ] ]
Contents: Acquired barcode data as a byte array
Token IDs
Token ID: di
Display Name: Device identifier
Token ID: manufacturing_date_original
Display Name: Manufacturing date
Token ID: expiration_date_original
Display Name: Expiration date
Token ID: lot_number
Display Name: Lot number
Token ID: serial_number
Display Name: Serial number
Token ID: mpho_lot_number
Display Name: Medical products of human origin (MPHO) lot number
Token ID: donation_id
Display Name: Donation ID number
Token ID: labeler_identification_code
Display Name: Labeler ID code
Token ID: product_or_catalog_number
Display Name: Product or catalog number
Token ID: unit_of_measure_id
Display Name: Unit of measure ID
Token ID: Quantity
Display Name: Quantity
Other Decode Tags
The decode-related data added to an intent bundle can be retrieved using specific string tags. Use the code below with the string tags in the section that follows.
Intent.getStringExtra()
Tag: LABEL_TYPE_TAG
Type: [String]
Name: "com.symbol.datawedge.label_type"
Contents: Barcode label type
Example: "LABEL-TYPE-EAN128"
Tag: DATA_STRING_TAG
Type: [String]
Name: "com.symbol.datawedge.data_string"
Contents: Acquired barcode characters
Example: "abcde12345"
Note: When multiple barcodes are acquired simultaneously, the decoded data is concatenated and sent out as a single string.
Tag: DECODE_DATA_TAG
Type: [byte [ ] ]
Name: "com.symbol.datawedge.decode_data"
Contents: Decoded data returned as a list of byte arrays.
Note: In most cases there will be one byte array per decode.
Other DataWedge Output Options:
- Keystroke - outputs acquired data as if the keyboard was pressed
- Internet Protocol - outputs data over a network using TCP or UDP
Related guides: